Setting up the CLI
You can download the most recent version from the GitHub releases page. Afterwards, you have to include the CLI into your path to use it from your shell, which heavily depends on your operating system and version thereof.
In any case, you can verify whether this worked correctly by typing recheck into a newly started shell. The output should show a help message like this:
$ recheck
Usage: recheck [--help] [--version] [COMMAND]
Command-line interface for recheck.
--help Display this help message.
--version Display version info.
Commands:
account Allows to log into and out of your account and show your API key.
help Displays help information about the specified command
commit Accept specified differences of given test report.
completion Generate and display an auto completion script.
diff Compare two Golden Masters.
ignore Ignore specified differences of given test report.
show Display differences of given test report.
version Display version info.
Linux
Unzip the downloaded archive to e.g. /opt/recheck.cli-1.5.0. Then add the following snippet to your .bash_profile and/or .bashrc:
export PATH="${PATH}:/path/to/recheck.cli/bin/"
Mac
If you use Homebrew, you can simply use our tap and install the CLI from there:
$ brew tap retest/tap
$ brew install recheck.cli
Alternatively, you can also install it manually as described in the Linux section.
Windows
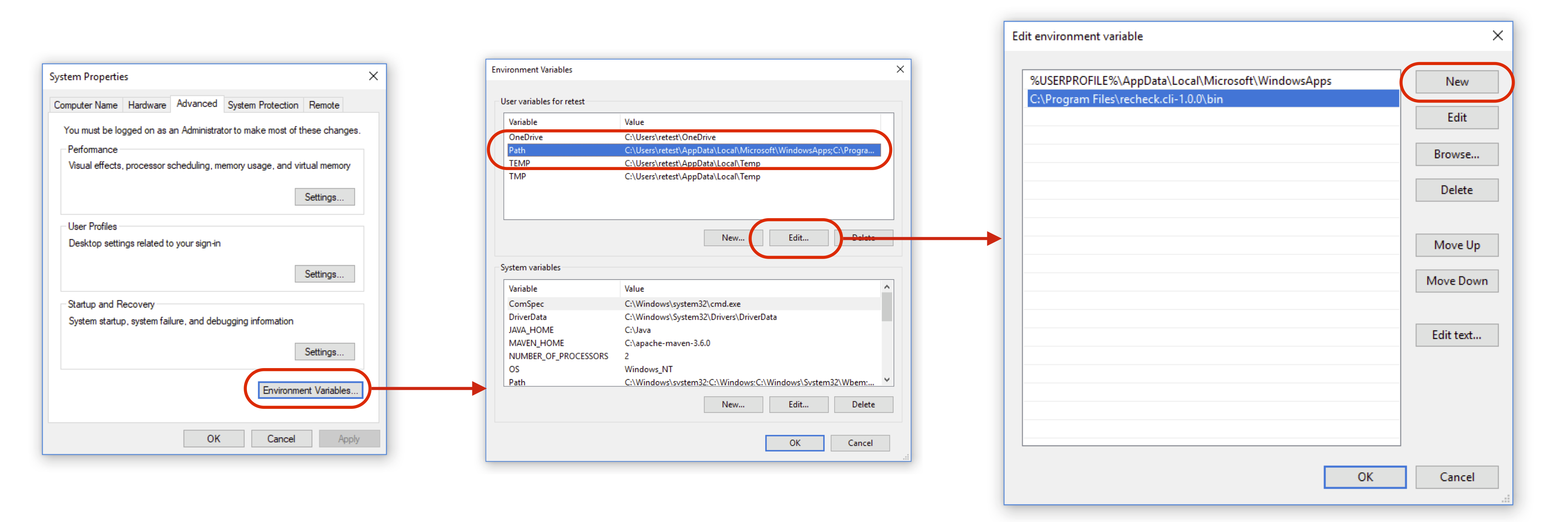
Unzip the downloaded archive to e.g. C:\Program Files\recheck.cli-1.5.0. To include the CLI into your path, you can follow this tutorial. On Windows 10, for instance, it works like this:
- Open settings.
- Enter "env" and select "Edit the system environment variables."
- Click on the tab "Advanced" -> "Environment Variables" -> "Path" -> "Edit" -> "New".
- Add the path to the
recheck/binfolder. If you installed it like above, that would beC:\Program Files\recheck.cli-1.5.0\bin\.
Enabling Shell Auto-Completion
You can obtain an auto-completion script for Bash and ZSH via the completion command. Simply add the resulting output to your .bash_profile and/or .bashrc, for example:
$ echo "source <(recheck completion)" >> ~/.bash_profile
Please note that this requires Bash version 4+ (macOS currently comes with version 3).